این مقاله توابع اعداد و کاربردهای آنها را در Tableau معرفی می کند. همچنین نحوه ایجاد یک محاسبه عدد را با استفاده از یک مثال نشان می دهد.
چرا از توابع عددی (Number Functions) استفاده کنیم؟
توابع عددی به شما امکان می دهد محاسبه مقادیر داده را در زمینه های خود انجام دهید. از توابع عددی فقط با فیلدهایی که دارای مقادیر عددی هستند می توان استفاده کرد.
به عنوان مثال ، ممکن است فیلدی داشته باشید که حاوی مقادیری برای واریانس بودجه شما باشد ، تحت عنوان Budget Variance.
یکی از این مقادیر ممکن است -7 باشد. برای برگرداندن مقدار مطلق آن عدد و سایر اعداد موجود در آن قسمت می توانید از تابع ABS استفاده کنید.
محاسبه ممکن است چیزی شبیه به این باشد:
برای خرید لایسنس تبلو Tableau کلیک کنید
Therefore, ABS(-7) = 7.
Number functions available in Tableau
| Function | Syntax | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ABS | ABS(number) |
Returns the absolute value of the given number. Examples: ABS(-7) = 7 The second example returns the absolute value for all the numbers contained in the Budget Variance field. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACOS | ACOS(number) |
Returns the arc cosine of the given number. The result is in radians. Example: ACOS(-1) = 3.14159265358979 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASIN | ASIN(number) |
Returns the arc sine of a given number. The result is in radians. Example: ASIN(1) = 1.5707963267949 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATAN | ATAN(number) |
Returns the arc tangent of a given number. The result is in radians. Example: ATAN(180) = 1.5652408283942 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATAN2 | ATAN2(y number, x number) |
Returns the arc tangent of two given numbers (x and y). The result is in radians. Example: ATAN2(2, 1) = 1.10714871779409 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CEILING | CEILING(number) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COS | COS(number) |
Returns the cosine of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example: COS(PI( ) /4) = 0.707106781186548 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COT | COT(number) |
Returns the cotangent of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Example: COT(PI( ) /4) = 1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DEGREES | DEGREES(number) |
Converts a given number in radians to degrees. Example: DEGREES(PI( )/4) = 45.0 Tableau |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DIV | DIV(integer1, integer2) |
Returns the integer part of a division operation, in which integer1 is divided by integer2. Example: DIV(11,2) = 5 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EXP | EXP(number) |
Returns e raised to the power of the given number. Examples: EXP(2) = 7.389 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLOOR | FLOOR(number) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HEXBINX | HEXBINX(number, number)
تبلو |
Maps an x, y coordinate to the x-coordinate of the nearest hexagonal bin. The bins have side length 1, so the inputs may need to be scaled appropriately. HEXBINX and HEXBINY are binning and plotting functions for hexagonal bins. Hexagonal bins are an efficient and elegant option for visualizing data in an x/y plane such as a map. Because the bins are hexagonal, each bin closely approximates a circle and minimizes variation in the distance from the data point to the center of the bin. This makes the clustering both more accurate and informative. Example: HEXBINX([Longitude], [Latitude]) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HEXBINY | HEXBINY(number, number) |
Maps an x, y coordinate to the y-coordinate of the nearest hexagonal bin. The bins have side length 1, so the inputs may need to be scaled appropriately. Example: HEXBINY([Longitude], [Latitude]) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LN | LN(number) |
Returns the natural logarithm of a number. Returns Null if number is less than or equal to 0. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LOG | LOG(number [, base]) |
Returns the logarithm of a number for the given base. If the base value is omitted, base 10 is used. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MAX | MAX(number, number)
تابع عددی تبلو |
Returns the maximum of the two arguments, which must be of the same type. Returns Null if either argument is Null. MAX can also be applied to a single field in an aggregate calculation. Examples: MAX(4,7) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIN | MIN(number, number) |
Returns the minimum of the two arguments, which must be of the same type. Returns Null if either argument is Null. MIN can also be applied to a single field in an aggregate calculation. Examples: MIN(4,7) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PI |
PI( ) |
Returns the numeric constant pi: 3.14159. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| POWER | POWER(number, power) |
Raises the number to the specified power. Examples: POWER(5,2) = 52 = 25 You can also use the ^ symbol: 5^2 = POWER(5,2) = 25 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RADIANS | RADIANS(number) |
Converts the given number from degrees to radians. Example: RADIANS(180) = 3.14159 توابع عددی (Number Functions) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ROUND | ROUND(number, [decimals]) |
Rounds numbers to a specified number of digits. The decimals argument specifies how many decimal points of precision to include in the final result. If decimals is omitted, number is rounded to the nearest integer. Example: This example rounds every Sales value to an integer: ROUND(Sales) Some databases, such as SQL Server, allow specification of a negative length, where -1 rounds number to 10’s, -2 rounds to 100’s, and so on. This is not true of all databases. For example, it is not true of Excel or Access. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIGN | SIGN(number) |
Returns the sign of a number: The possible return values are -1 if the number is negative, 0 if the number is zero, or 1 if the number is positive. Example: If the average of the profit field is negative, then SIGN(AVG(Profit)) = -1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIN | SIN(number) |
Returns the sine of an angle. Specify the angle in radians. Examples: SIN(0) = 1.0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SQRT | SQRT(number) |
Returns the square root of a number. Example: SQRT(25) = 5 Number Functions |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SQUARE | SQUARE(number) |
Returns the square of a number. Example: SQUARE(5) = 25 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TAN | TAN(number) |
Returns the tangent of an angle. Specify the angle in radians.. Example: TAN(PI ( )/4) = 1.0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ZN | ZN(expression) |
Returns the expression if it is not null, otherwise returns zero. Use this function to use zero values instead of null values. Example: ZN([Profit]) = [Profit] |
لایسنس تبلو
برای مشاهده ویدیوی آموزشی Calendar in Tableau در یوتیوب لینک زیر را کلیک کنید ⇓
⇐ ⇐ How to Create a Calendar in Tableau
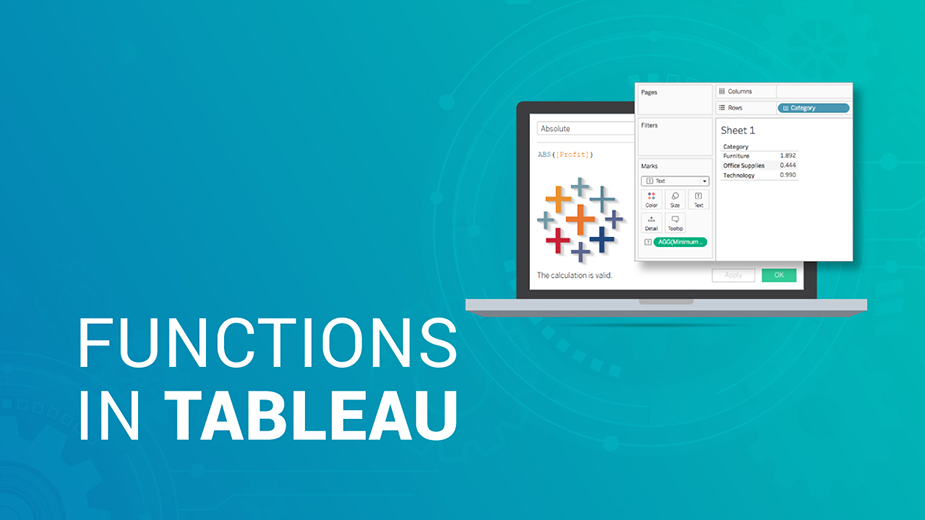
یک تابع عددی (Number Functions) ایجاد کنید
- برای یادگیری نحوه ایجاد محاسبه اعداد ، مراحل زیر را دنبال کنید.
- در Tableau Desktop ، به منبع داده ذخیره شده نمونه – Superstore متصل شوید که همراه با Tableau است.
- به یک صفحه کار بروید و Analysis> Create Field محاسبه شده را انتخاب کنید.
در ویرایشگر محاسبه باز شده ، موارد زیر را انجام دهید:
قسمت محاسبه شده را معامله حداقل فروش بنامید
فرمول زیر را وارد کنید:
پس از پایان ، تأیید را کلیک کنید.
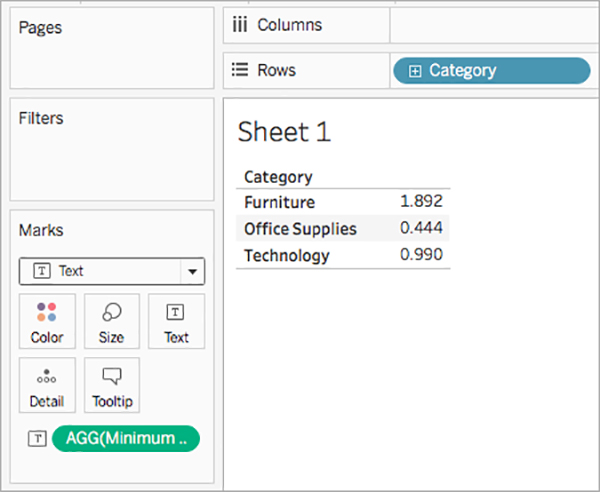
محاسبه عدد جدید در بخش اندازه گیری ها در قسمت داده ظاهر می شود. درست مانند سایر زمینه های خود ، می توانید از آن در یک یا چند تجسم استفاده کنید.
هنگامی که حداقل فروش در متن روی کارت Marks در صفحه کار قرار می گیرد ، نام آن به AGG (حداقل فروش) تغییر می یابد ، که نشان می دهد دیگر نمی توان آن را جمع کرد ، زیرا در پایین ترین سطح جزئیات جمع شده است ( کوچکترین ارزش فروش برای تمام سوابق).
این مثال حداقل فروش در هر گروه را نشان می دهد.
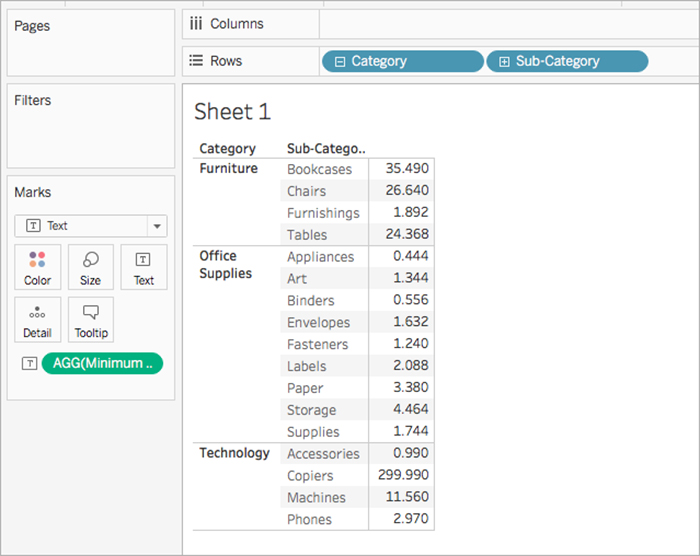
هنگامی که زیر مجموعه به نمایش در می آید ، حداقل فروش برای هر زیر مجموعه نشان داده می شود.
دوره آموزشی هوش تجاری با Tableau »کلیک کنید« یک برنامه جامع است که بر توسعه مهارت در تجزیه و تحلیل دادهها، تجسم و گزارش سازی و گزارش دهی و دشبوردسازی با استفاده از ابزار Tableau تمرکز دارد.
سپاسگذاریم از وقتی که برای خواندن این مقاله گذاشتید
.
برای خرید لایسنس تبلو کلیک کنید
.
برای مشاهده ویدیوهای آموزشی داده کاوی و هوش تجاری ما را در شبکه های اجتماعی دنبال کنید
Youtube Chanel :VISTA Data Mining
Aparat Chanel: VISTA Data Mining
Instagram Chanel: VISTA Data Mining
Telegram Chanel: VISTA Data Mining
Linkedin Chanel: VISTA Company